Utility of sas floor and sas ceil functions.
Floor integer function sas.
The int function rounds towards zero.
If the value of argument is positive the int function has the same result as the floor function.
The round function rounds to the nearest integer.
The floorz function does not fuzz the result.
The int function returns the integer portion of the argument truncates the decimal portion.
The floor function fuzzes the results so that if the results are within 1e 12 of an integer the floor function returns that integer.
Unlike the floorz function the floor function fuzzes the result.
The floorz function uses zero fuzzing.
In mathematics and computer science the floor function is the function that takes as input a real number and gives as output the greatest integer less than or equal to denoted or similarly the ceiling function maps to the least integer greater than or equal to denoted or.
If the argument s value is within 1e 12 of an integer the function results in that integer.
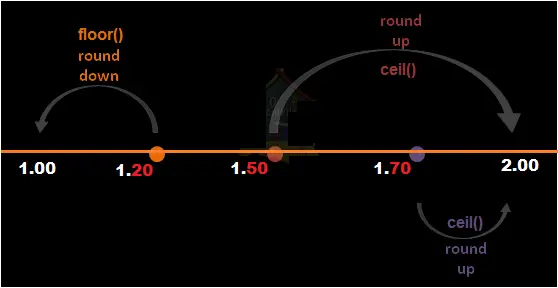
The ceil function rounds up.
The floor function rounds down.
It will be easier to understand their role now that you understood the explanation above about sas round function.
For example and while.
Briefly i want to mention the sas floor and sas ceil functions.
Therefore with the floorz function you might get unexpected results.
The floor function returns the largest integer that is less or equal to the argument.
If sas reads y with a different informat or if a program other than sas reads y then there is no guarantee that the characters 0 3 would produce a value of exactly 3 10.
If the argument s value is within 1e 12 of an integer the function results in that integer.
The int function returns the integer portion of the argument truncates the decimal portion.
If the argument s value is within 1e 12 of an integer the function results in that integer.
If the argument s value is within 10 12 of an integer the function results in that integer.
If the value of argument is negative the int function has the same result as the ceil function.
The functions that perform rounding are the same in the data step as in the sas iml language.
If the argument is within 1e 12 of an integer the floor function fuzzes the result to be equal to that integer.
If the value of argument is negative the int function has the same result as the ceil function.
When the rounding unit is the reciprocal of an integer the round function computes the result by dividing by the integer.
Round treats the rounding unit as a.
If the value of argument is positive the int function has the same result as the floor function.
In the case below it will return 2.